立夏

15時31分立夏,太陽黄經45度。
夏天開始,雨水增多,農作物生長漸旺,田間工作日益繁忙。
2016-17年度天文課程 (中學天文課程)

中學天文課程
日期:
2017.05:05(五),12(五),16(二),22(一),26(五)
2017.06:02(五),09(五),16(五),20(二)
時段:14:00 ~ 16:30
日期:2016.10.25(二) ~ 2017.06.27(二) (指定日期晚間可選)
2016.10.25(二)
2016.10:26(三),28(五)
2016.11:14(一),21(一),22(二),28(一),29(二)
2016.12:06(二),20(二),21(三)
2017.01:05(四),06(五),09(一),10(二),16(一),24(二)
2017.02:07(二),22(三),24(五)
2017.03:03(五),08(三),13(一),14(二),20(一),21(二),28(二)
2017.04:05(三),07(五),10(一),11(二),25(二)
2017.05:12(五),16(二),22(一),23(二),25(四),31(三)
2017.06:01(四),02(五),05(一),08(四),12(一),15(四),19(一),27(二)
時段:19:00 ~ 21:30
地點:荃灣荃錦公路101號 嗇色園可觀自然教育中心暨天文館
◎高中天文課程
對象: 中四至中六級物理科學生
◎日間/晚間天文活動
對象:中一至中六學生
名額:每節45
免費課程,惟不包括交通費,2016.10.03(一) 09:00起,參加者必須報名,2016.10.13(四) 13:00截止,抽籤選拔
【訊息由張詠倫提供】
此活動由可觀自然教育中心暨天文館主辦。
星系團MACSJ0329-0211中央巨大橢圓星系的近期恆星形成史

Public Seminar of RPg Student:- Recent Star Formation History of the Central Giant Elliptical Galaxy of the Cluster MACSJ0329-0211
A number of cluster central giant elliptical galaxies(a.k.a. brightest cluster galaxies, BCGs) exhibit recent or ongoing star formation that is most clearly revealed in the UV continuum. The nature of this star formation activity (i.e., origin of the star-forming gas, star formation rate over time) is poorly understood. The best data currently available for elucidating the star formation history of BCGs come from the Cluster Lensing And Supernova survey with Hubble(CLASH), which spans wavelengths from the near-UV to the near-IR in 16 filters. Previous studies using this data have used only the UV filters to estimate star formation rates(SFR) in this BCG assuming a certain star formation history(i.e., nearly constant SFR over 100 Myr). Here, we derive the spatially-resolved spectral energy distribution (SED) of the relatively young stellar population so as to infer its star-formation history through population synthesis modeling. We anticipate our work to set a benchmark for what can be learnt from this unique and high quality data set having unprecedented wavelength coverage.
To obtain the SED of the young stellar population, we first have to subtract the light contributed by the old stellar population in every filter band. To model the 2-dimensional light distribution of the old stellar population, we used images in the longest-wavelength bands where the old stellar population dominates the overall light. In doing so, we found it necessary to mask out nearby cluster members, as well as both the young stellar population and dust based on color images of the BCG. The model parameters for the 2-D light distribution of the old stellar population thus derived was consistent among the reddest filter bands, allowing us to construct a wavelength-averaged model applicable to all filter bands. The images obtained after subtracting the model for the old stellar population have good consistency with the spatial distribution of the young stellar population that dominates the UV images, as well as color images of the BCG.
To make a preliminary look and to obtain global view of the data, we compared a color-color diagram (constructed from three line-free filters) of the young stellar population with population synthesis model. The results, which are only weakly sensitive to metallicity, implies ages ranging from ~10 Myr to nearly 1Gyr for the young stellar population.
We are now in the process of modeling the entire SED to determine: (i) whether the ages thus inferred are compatible with that those inferred from the color-color diagram; (ii) the degree to which we can break the age-metallicity degeneracy; (iii) whether it is necessary to include dust extinction, and the extra degree of degeneracy in doing so.
時間:2017.05.04(四) 10:00
地點:香港大學 莊月明物理樓105室
講者:Junhao LI (香港大學)
語言:英語
免費會議,歡迎參加
#119
此活動由香港大學物理系主辦。
富能毫秒脈衝星的X射線和γ射線觀測

Public Seminar of RPg Student:- X-ray and Gamma-ray Observations of Energetic Millisecond Pulsars
Pulsars are fast spinning neutron stars produced by supernova explosions of massive stars and they possess extremely high magnetic fields from 108G to 1012G. Millisecond pulsars (MSPs) are fastest-rotating pulsars with periods from about one to several tens of milliseconds. They are believed to be spun up in binary systems. Their surface magnetic fields are small compared with normal pulsars, but they usually possess large magnetic fields near the outer gaps due to their small light cylinder radii. This makes some MSPs have broadband emission properties similar to young pulsars.
This project aims to understand the high-energy emission properties of energetic MSPs. the speaker focus on three energetic rotation-powered MSPs─B1937+21, B1821-24 and J0218+4232. Firstly, he will talk about the X-ray spectra of these MSPs. Then, the speaker will report the results of timing analysis using NuSTAR data. he will also talk about my research plan, to focus on analyzing gamma-ray data and build a theoretical model to explain the emission.
時間:2017.05.04(四) 10:30
地點:香港大學 莊月明物理樓105室
講者:Wenchao WANG (香港大學)
語言:英語
免費會議,歡迎參加
#119
此活動由香港大學物理系主辦。
光從哪裡去了?哈勃望遠鏡前緣場中透出受抑高紅移星系形成的證據

Public Seminar of RPg Student:- Where’s the Light? – Evidence for Suppressed High-redshift Galaxy Formation from the Hubble Frontier Fields
The standard Cold Dark Matter (CDM) model predicts that galaxies form hierarchically, resulting in an increasing number of galaxies towards lower masses and hence fainter luminosities at all redshifts since the onset of galaxy formation. In the Local Universe, such a dependence had been found for luminosities as low as dwarf spheroidal galaxies, the least massive galaxies known. A similar trend had also been confirmed in the early universe through blank field surveys, which provide a limiting rest-frame UV absolute magnitude of MUV ~ -17 at redshifts z > 4. Does this trend of increasing galaxy space density continue to even lower luminosities as predicted by the CDM model, or eventually turn over as predicted by competing models such the Wave Dark Matter (ψDM) model?
To probe even fainter luminosities than is possible through blank field surveys, we took advantage of gravitational lensing provided by massive galaxy clusters that boosts otherwise undetectable faint galaxies to above the intrinsic survey flux limit. Our sample comprises ~600 dropout galaxies identified in five galaxy cluster fields and their adjacent blank fields (observed simultaneously) from the Hubble Frontier Fields program. These galaxies are magnified in brightness by as high as ~100×, thus allowing us to probe approximately five magnitudes deeper than the intrinsic survey limit. Because a given solid angle in the sky is similarly magnified, the volume of space probed decreases in proportion to the magnification. This effect, however, is countered by the expected increase in space density of less luminous galaxies as predicted by the CDM model.
Contrary to such expectation, we discovered a significant deficit of highly magnified galaxies in the data relative to the CDM prediction, reflecting that the diluted apparent galaxy density from the magnified sky area heavily outweighs the addition of faint galaxies brought above the flux limit. This result was found to be in >4σ tension with the standard CDM model, indicating a slow rollover in the faint-end UV luminosity function as is predicted by the ψDM model. In this alternative model, the formation of low-mass DM halos, which seed the growth of faint galaxies, is suppressed by the quantum pressure arising from interfering ultralight dark matter waves with parsec-scale de Broglie wavelengths.
Through a comparison with state-of-the-art ψDM simulations, we found that our results are compatible with the model predictions for a DM boson mass of ~10^-22 eV. The inferred boson mass is consistent with that deduced independently for producing the large constant-density DM cores of local dwarf spheroidal galaxies. In addition, our results also show a marked transition (stronger decline towards higher redshifts) in the cosmic star formation rate density at z ~ 8, a similar redshift as the instantaneous epoch of reionization at z = 8.2 reported by Planck.
時間:2017.05.04(四) 11:30
地點:香港大學 莊月明物理樓105室
講者:Yi Lok Enoch LEUNG (香港大學)
語言:英語
免費會議,歡迎參加
#119
此活動由香港大學物理系主辦。
軒轅十四合月
18時14分,軒轅十四在月球北面0.52度
上弦

10時47分
北河三合月
03時55分,北河三合月,北河三在月球北9.77度
灶神星合月
14時32分,灶神星在月球北面7.22度。
水星留
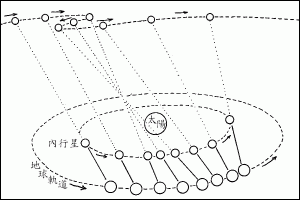
22時21分水星留,之後由逆行轉為順行